
Technology
Integrated Digital Delivery (IDD) for the Built Environment
October 14, 2021
Enhanced communication and trust are paramount across a diverse portfolio of data and applications in the construction industry. How does one best demonstrate the various solutions and updated data sources to all stakeholders across the design process?
An Integrated Digital Delivery (IDD) workflow enables seamless project execution across the value chain and embraces the Single Source of Truth (SSOT) concept by leveraging cloud-based technologies through a Common Data Environment (CDE) setup. In addition, Building Information Modelling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) processes are the key enablers that account for the success of IDD.
An Integrated Digital Delivery (IDD) workflow enables seamless project execution across the value chain and embraces the Single Source of Truth (SSOT) concept by leveraging cloud-based technologies through a Common Data Environment (CDE) setup. In addition, Building Information Modelling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) processes are the key enablers that account for the success of IDD.
What is IDD?
Integrated Digital Delivery (IDD) is a transformative approach offering project teams solutions that not only revolutionise the way they create and design built environment projects, addressing long-standing productivity challenges in the construction industry, but also delivers the smarter buildings that communities of the future demand.
Construction management requires updated communication between various stakeholders regardless of project type: industrial, retail, commercial, residential, civil, etc. The outcome-based focus of IDD workflows enable efficient time management, ease of business and sustainability of construction with a potential for cost reduction.
The combining of digital design, fabrication, construction, asset delivery and management is the key appeal of Integrated Digital Delivery.

The four main areas covered by IDD (Building and Construction Authority).
Digital Design

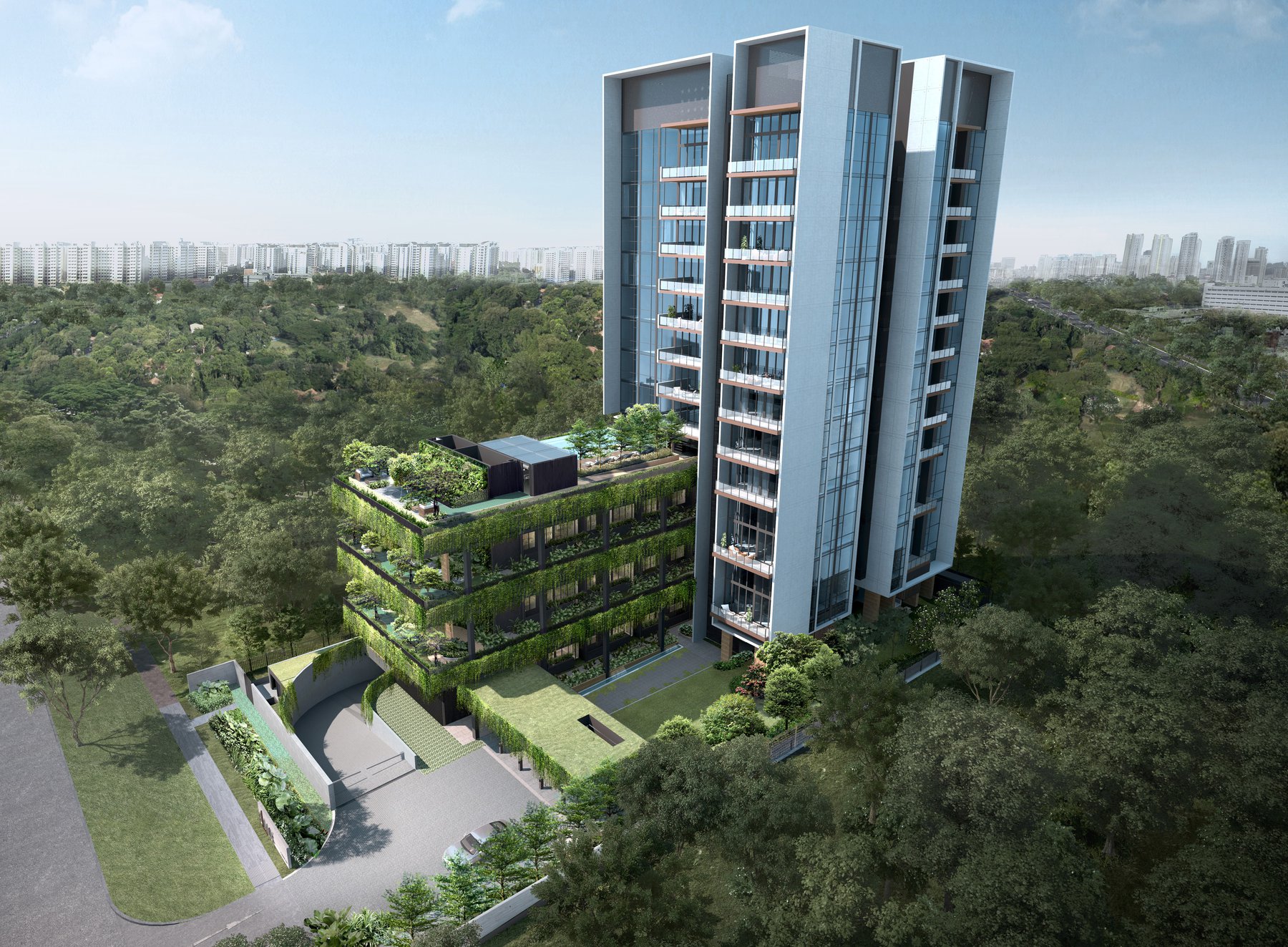
Digital design consists of initial planning from the data collected in pre-construction operations stored at the Common Data Environment (CDE) platform.
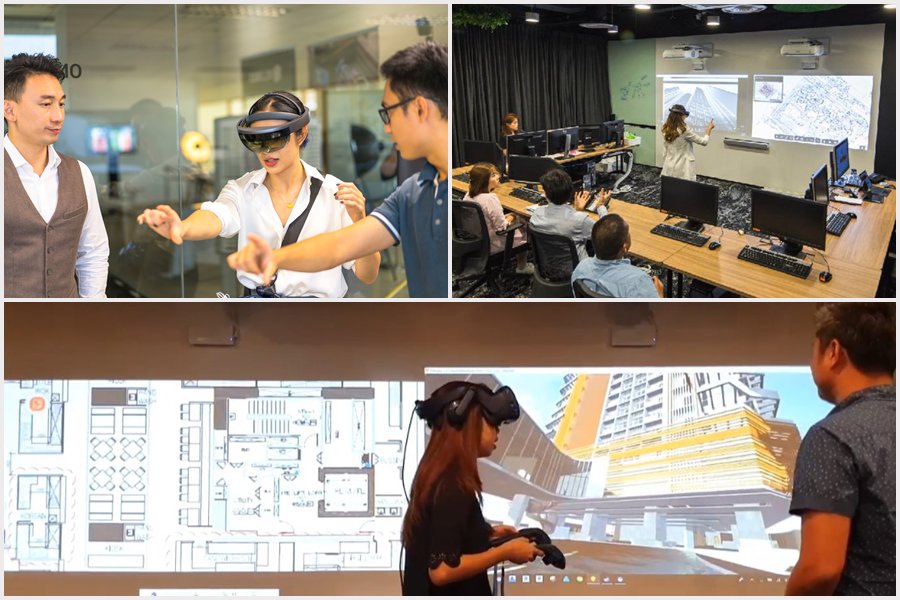
Advanced visualisation solutions such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR) allow designers to cover digital models on verified sites and facilitates stakeholders in viewing how the elements of a building project will appear in the real world. The virtual environments eliminate the need for physical blueprints and help project teams and stakeholders navigate the challenges and issues that are considered pain points, such as minimising errors and troubleshooting issues, before starting the construction work. This prior addressing of design issues helps teams coordinate and collaborate better.
With the use of Virtual Reality (VR), project teams and stakeholders can easily navigate the challenges and issues that are considered pain points in the construction industry. Mixed Reality (MR) and real-time rendering solutions increase the efficiency of construction teams.
Advanced visualisation solutions such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR) allow designers to cover digital models on verified sites and facilitates stakeholders in viewing how the elements of a building project will appear in the real world. The virtual environments eliminate the need for physical blueprints and help project teams and stakeholders navigate the challenges and issues that are considered pain points, such as minimising errors and troubleshooting issues, before starting the construction work. This prior addressing of design issues helps teams coordinate and collaborate better.
With the use of Virtual Reality (VR), project teams and stakeholders can easily navigate the challenges and issues that are considered pain points in the construction industry. Mixed Reality (MR) and real-time rendering solutions increase the efficiency of construction teams.
Digital Fabrication
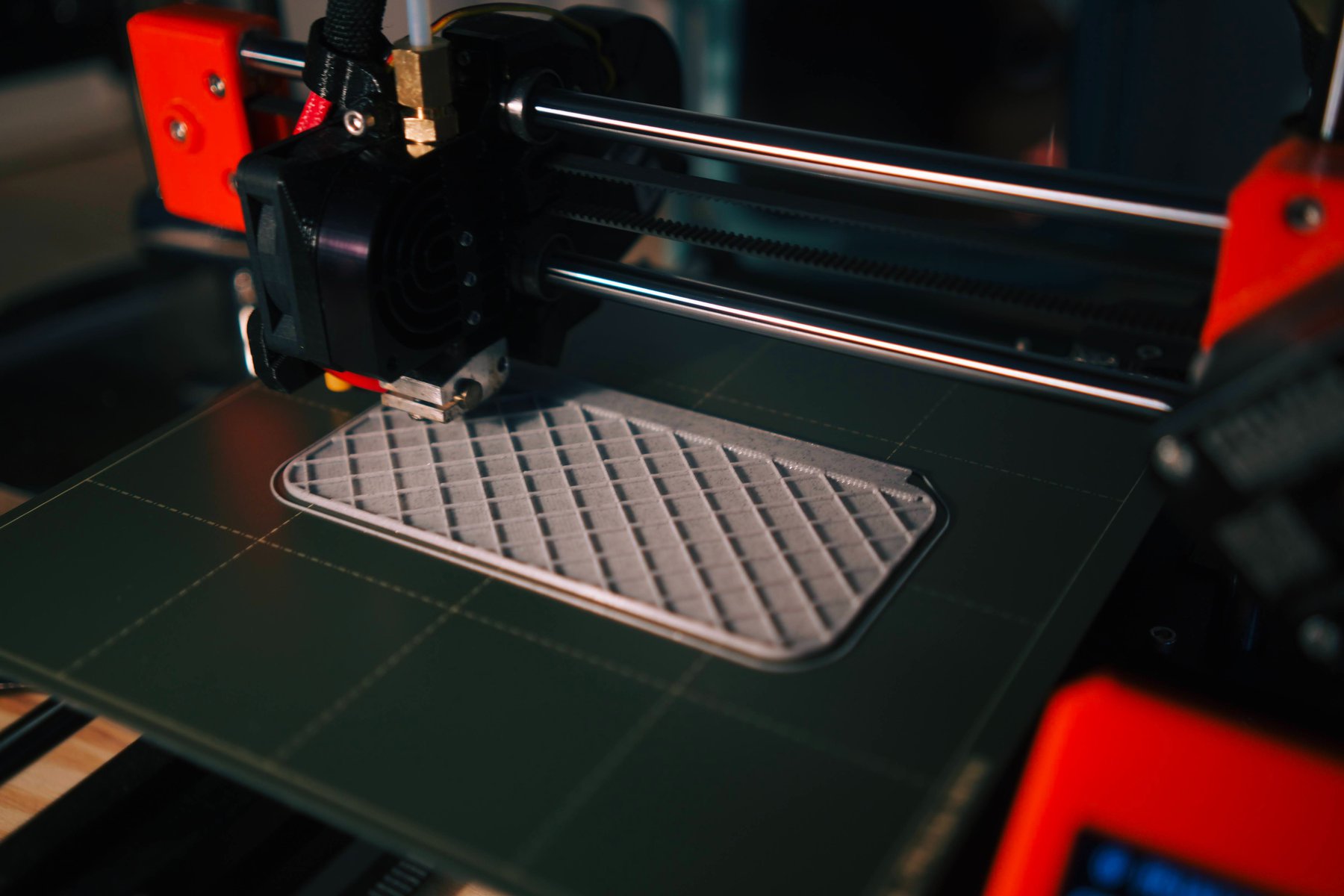

Digital fabrication is a process where machines are programmed to make compatible products from digital designs, essentially transforming data into objects.
CNC machining, laser cutting, and 3D printing are vital aspects of digital fabrication. CNC machining and laser cutting are subtractive manufacturing processes that carve out solid material to generate the final product. 3D printing however, is an additive manufacturing process that creates a product by adding material in layers from the bottom up.
Digital construction is the application of digital solutions to improve the process of managing and delivering the desired built environment.
A Common Data Environment (CDE) platform helps clients, architects, engineers, builders and stakeholders involved in a project, collaborate in an interconnected and coordinated way. CDE makes collection, organisation, and distribution of data between different teams a safe and streamlined process, which is essential for developing BIM projects.
CNC machining, laser cutting, and 3D printing are vital aspects of digital fabrication. CNC machining and laser cutting are subtractive manufacturing processes that carve out solid material to generate the final product. 3D printing however, is an additive manufacturing process that creates a product by adding material in layers from the bottom up.
Digital Construction
Digital construction is the application of digital solutions to improve the process of managing and delivering the desired built environment.
A Common Data Environment (CDE) platform helps clients, architects, engineers, builders and stakeholders involved in a project, collaborate in an interconnected and coordinated way. CDE makes collection, organisation, and distribution of data between different teams a safe and streamlined process, which is essential for developing BIM projects.
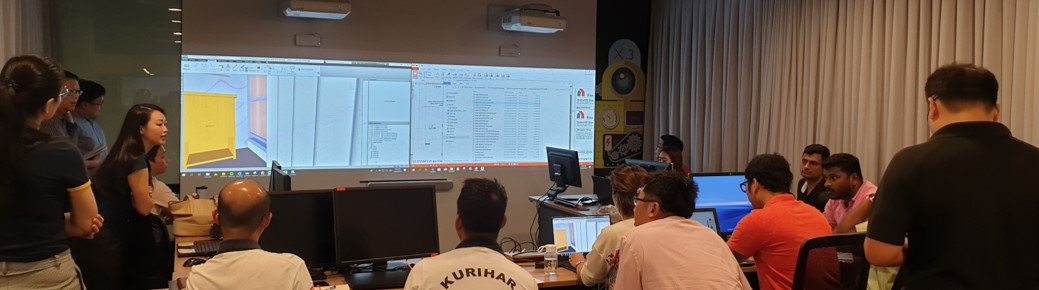
An ICE session in progress.
Integrated Concurrent Engineering (ICE) and digital virtual mock-ups help stakeholders to review the design before on-site construction begins. Digital tools and platforms can be used to facilitate the visualisation of element properties, extracting measurements and making changes in both 3D and 2D views. ICE sessions were normally performed in meeting rooms, co-located spaces (Big room concept) or site offices. However, when the pandemic hit, teams transitioned to virtual environments like Zoom, Microsoft Teams or other virtual meeting spaces for ICE sessions.
Digital Asset Delivery and Management
Digital asset delivery and management in IDD is the ability to monitor and manage valuable company assets for each project digitally. It encourages collaboration, streamlines workflows and team coordination with projects and clients.
● Evaluation or assessment
● Preparation for the transition/project pre-planning
● Execution of the plan, design, and construction
● Operations and maintenance
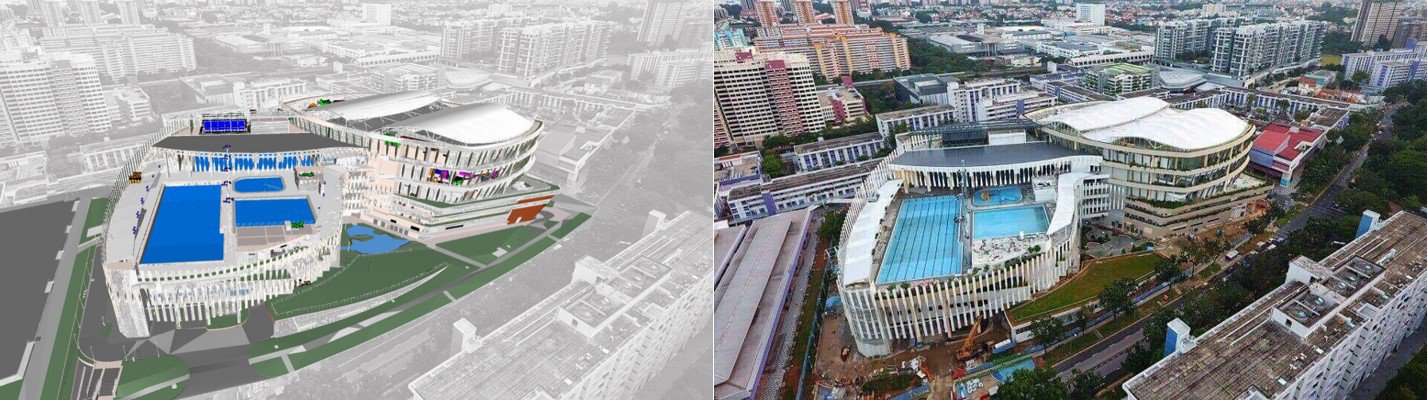

Virtual Design & Construction (Digital Twin) of Heartbeat@Bedok.
Non-proprietary data formats such as Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie) helps the sharing of BIM data between stakeholders for the purpose of asset management much smoother. COBie addresses the issue of interoperability of BIM data from construction to operations, ensuring there is no information loss and maintains the consistency of the data’s structure.
From warehouse inventories to work orders, the use of BIM and COBie help to track assets and personnel with precision. Essentially, this will optimise asset management operations, repair, replacement, cost savings and reduce environmental impacts.
From warehouse inventories to work orders, the use of BIM and COBie help to track assets and personnel with precision. Essentially, this will optimise asset management operations, repair, replacement, cost savings and reduce environmental impacts.
Impact and Adoption
Adopting IDD has achieved a significant positive impact in many firms. Despite difficulties due to the global economic shock from the pandemic in early 2020, construction industry investments have bounced back in the latter half of the financial year. IDD implementation involves training staff and embracing secure data management.
The Building and Construction Authority (BCA) recently recognised ONG&ONG Group for the exemplary implementation of IDD within the organisation. The Platinum Award from BCA was based not only on the Group’s adoption of technology into work processes but also how the organisation and its employees integrate IDD into the culture of the company.
Conclusion
Highly complex projects in the construction industry come with their own set of risk factors, which at times lead to costly delays. IDD offers practical, real-time data to help all stakeholders in a project achieve better efficiency. This data sharing environment improves construction workflows and shortens project life cycles, thus leading to better outcomes.